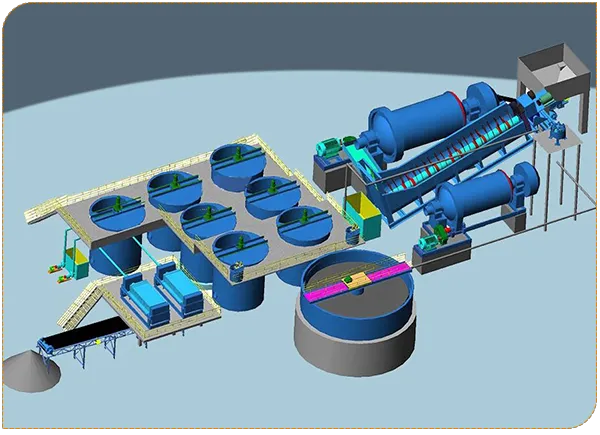
Carbon-in-Pulp (CIP) and Carbon-in-Leach (CIL) represent two highly efficient processes widely employed in modern gold extraction, centred on utilising activated carbon to “capture” gold from cyanide-leached pulp. These methods—particularly CIL—significantly enhance gold recovery rates and reduce costs by closely integrating leaching with adsorption steps.
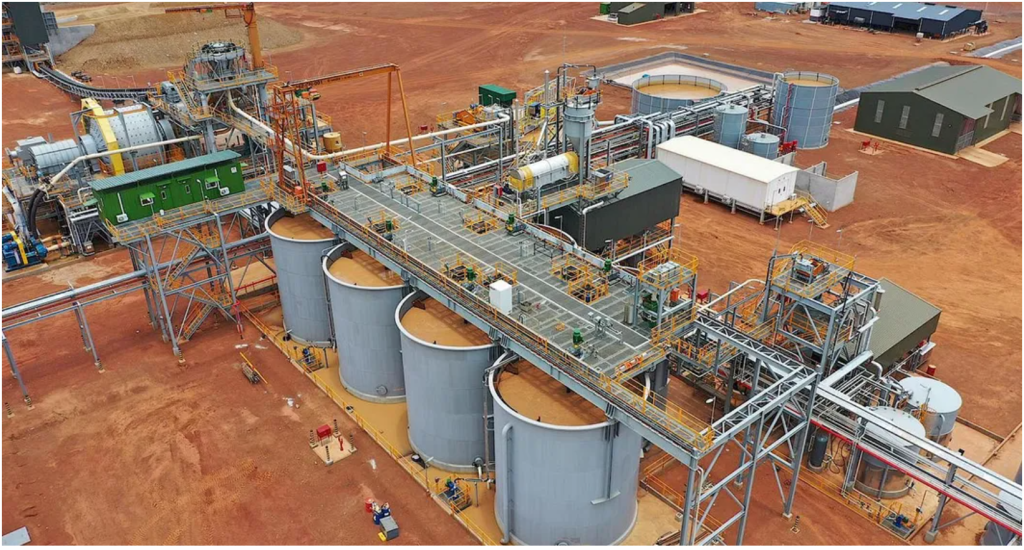

Gold CIP (Carbon in Pulp) refers to the process of gold extraction from carbon pulp, which is a hydrometallurgical process of extracting gold through cyanide leaching and activated carbon adsorption. It is suitable for treating middle and low grade ore, sulfide bearing or complex gold ore.
Gold CIL is a process that improved on the basis of CIP process. This process simultaneously leaches and adsorbs gold and finds wide application in treating low-grade gold ores or tailings.
1.Preparation of Leaching Slurry
Gold ore is crushed and ground to a particle size suitable for cyanide leaching. The process removes impurities (such as sawdust) from the slurry to prevent carbon screens from clogging.
2.Cyanide Leaching
The ore slurry is stirred and leached using chemical reagents.
3.Activated Carbon Adsorption
Operators transfer the cyanide-leached pulp into adsorption tanks, where activated carbon adsorbs the dissolved gold to form gold-bearing carbon.
4.Gold-Bearing Carbon Desorption
Carbon screens separate the gold-bearing carbon from the pulp, and then the desorption system desorbs the gold complexes.
5.Gold Slime Recovery via Electrolysis
Recover precious metal solutions from desorbed gold-adsorbed carbon through electrolysis, ultimately yielding gold slime.
6.Regeneration of Desorbed Carbon
Treated to remove impurities, desorbed activated carbon may be recycled into adsorption tanks for reuse.
7.Leachate Treatment
Leachate may undergo acidification followed by absorption of volatile alkalis.
We are a professional machinery manufacturer that produces and sells our own products.
You can bring materials to the factory to test the machine
We will customize the solution according to your needs
60S Quick response
Minutes Technical reply
Hours design proposal
 whatsApp
whatsApp