Amalgamation is a traditional method of recovering gold by selective wetting of mercury with gold particles to form an amalgam.
Gold Amalgamation Production Line is a traditional method of gold extraction that utilizes mercury to form amalgams (gold-mercury amalgams) with gold. This method's long-standing simplicity makes it ideal for recovering coarse free gold.
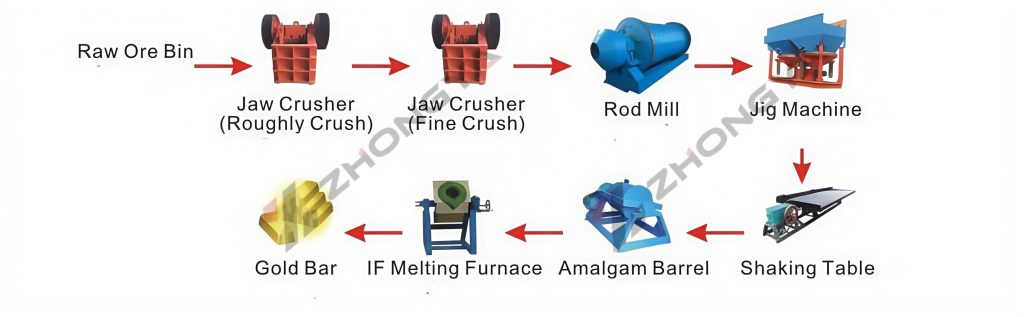
Amalgamation divides into internal and external methods, each with distinct operational parameters, applications, and recovery rates.
1.Internal Amalgamation
Applicable Ores: Ores containing coarse-grained gold (>0.1mm), such as alluvial gold ore or crushed vein gold ore.
Process Flow
Crushing and Grinding: The ore is crushed until the gold particles are dissociated (particle size <1mm).
Amalgamation:
Mercury (0.1%-1%) is added to the ball mill, amalgamating cylinder or Millstone.
During the milling process, the gold particles come into full contact with the mercury to form an amalgam.
Amalgam Collection:
The cleaning procedure flushes the equipment with water, followed by recovery of the silver-white amalgam.
Amalgam distillation:
Heating to 400~500℃, mercury evaporation and recovery, the remaining crude gold further purification.
Advantages:
High recovery rate (60%~90%).
Suitable for large-scale continuous production.
Disadvantages:
High consumption of mercury and high risk of pollution.
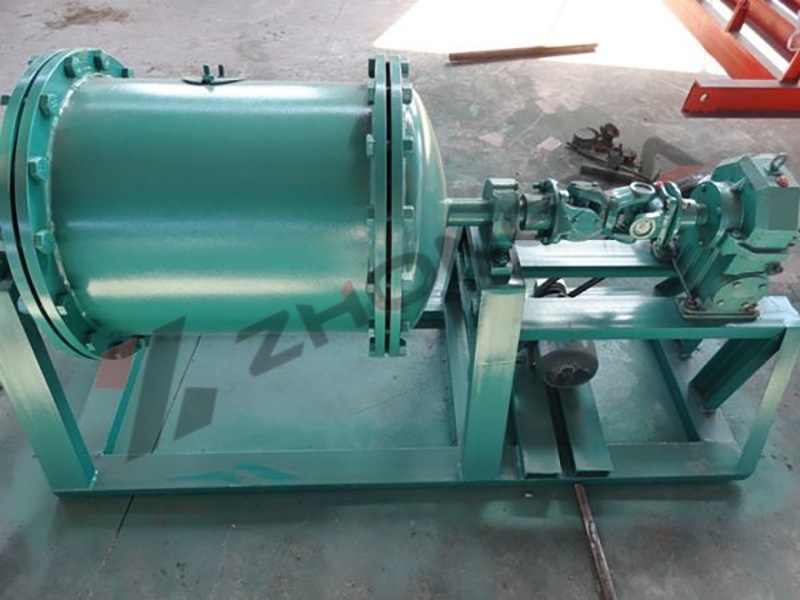

2.External Amalgamation
Applicable Ore: Alluvial gold ore or slurry containing coarse-grained gold.
Process Flow
Ore Preparation: Slurry is enriched by chute, shaking table and other equipment.
Mercury plate adsorption:
Apply a thin, even layer of mercury onto a copper plate (pre-plated with mercury) or a dedicated mercury plate.
During slurry transit over the mercury plate, the liquid mercury selectively entraps liberated gold particles, initiating amalgamation.
Scraping of the amalgam:
The refining process involves regularly scraping amalgam deposits from the plate, followed by press-filtration to separate residual mercury.
Gold Distillation:
Heated distillation to separate mercury from gold.
Advantages:
Simple operation, suitable for small scale or secondary recovery.
Low mercury consumption.
Disadvantages:
Low recovery (30% to 60%).
Loss of fine-grained gold.
We are a professional machinery manufacturer that produces and sells our own products.
You can bring materials to the factory to test the machine
We will customize the solution according to your needs
60S Quick response
Minutes Technical reply
Hours design proposal
 whatsApp
whatsApp